Employee remuneration expectations – frequency or value?
Employee Remuneration Expectations – managing for engagement
In this article on employee expectations we look at ‘remuneration expectations’ and how they impact employee engagement.
We all want to be paid a fair wage for a fair day’s work and remuneration is certainly near the top of employee expectations. It is not, however, the primary motivator for a good many of us and vies for position with the quality of the workplace environment, being appreciated and having a competent, responsive manager.
The organisational view
Most employees understand that a company has different pay grades and that they cannot expect to earn more than someone else who does the same job. Having said that, the increasing problem of those being paid below the living wage can create tensions for many companies.
If you want to earn a higher salary, the excepted way of doing it is to take on more responsibility and possibly undertake further training.
For those who want higher pay, this can often be the sticking point, particularly if they are not self-motivated enough to develop their own careers.
The individual’s remuneration expectations
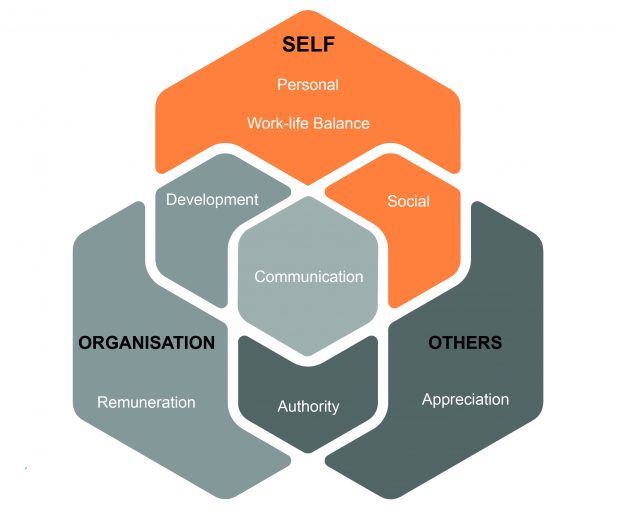
Asking the right questions, and analysing each individual employee’s real engagement factors ensures managers and the wider organisation provide an environment that retains their best talent.

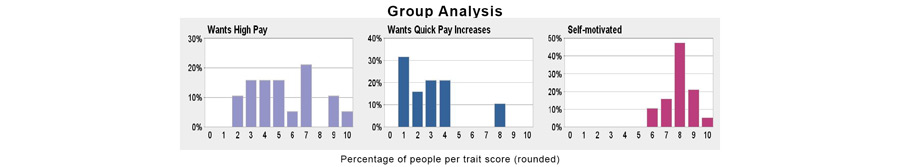
Remuneration Expectations
Employee remuneration expectations can vary depending on the amount of pressure they are under, the type of work they have to do and the environment they work in. Even individuals in a particular office might have different views about whether they are paid enough or not.
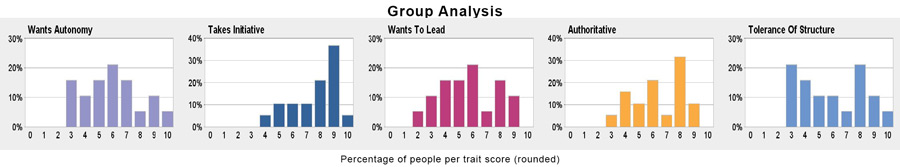
Wants High Pay
- The desire to earn greater remuneration
- A competitive and career minded individual will more likely see their worth in the amount that they are paid, or have the potential of earning, compared to someone who just wants to come in and get their allotted work done.
- Wanting higher pay can be a signifier of personal ambition which could mean that a top performing team member may look elsewhere if they don’t achieve what they hope for. It can also be a pipe dream where an individual wants more pay but is not prepared to get the work and study done to reach their target.
Wants Quick Pay Increases
- The desire to have an employer who offers relatively frequent pay increases
- Linked to the desire for higher pay, is the need for them to be delivered quickly. Most businesses have a yearly incremental increase in salary but that might not be enough for some employees. This could be a sign that they are moving quickly up the ladder or it could be that their ambitions are outstripping their actual ability.
- Impatience can be a virtue but it can also signify that an employee is more likely to look round at other companies rather than stay put and contribute to the development of an organisation.
Self-Motivated
- The drive to achieve including taking initiative, wanting challenge, and being enthusiastic about goals
- Those who want to develop their own careers necessarily have to be self-motivated. This can be a difficult one to gauge particularly if the employee is deluding themselves about just how much they have in the tank for climbing the corporate ladder.
- There may well be good signs for self-motivated behaviour such as learning new key skills and being open to challenges and these can mark out an employee as someone who needs to be handled sympathetically and nurtured if they are to stay with the company.
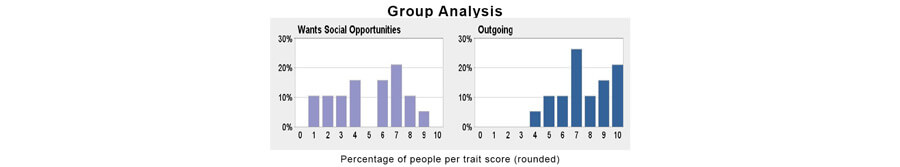
Does everyone in the group have the same remuneration expectations?
Finding out what employee’s remuneration expectations are can be highly enlightening; by using Harrison Assessments engagement and retention analytics we can explore them in detail.
What can we interpret for this group?
- This group considers earning higher pay levels to be only moderately important and thus, it is only moderately important to carefully explain how higher pay can be achieved.
- This group considers quick pay increases to be unimportant. Consequently, this group is probably not going to be too impatient about achieving higher pay.
- This group has a strong tendency to be self-motivated independent of consideration about remuneration.
Using Harrison Assessments Talent Solutions to understand remuneration expectations
Managers can measure an number of key employee expectations, the intrinsic behaviours that drive individual and group engagement. This helps to understand any differences between an employee as well as looking at the overall group or team’s expectations. These insights facilitate the essential dialogue between employee and manager, fostering a shared responsibility for engagement to build a culture of employee engagement.
Managers can use the Manage, Develop and Retain report as a guide to getting the best performance out of an individual member of their team, and shows how mis-matched communication and management styles could potentially demotivate a talented employee. Instead the report suggests how best to develop and engage the employee, what type of tasks to delegate and behaviours to watch out for that could impede performance.
Employee Engagement White Paper
- This employee engagement white paper will outline why this is the case and what is needed to achieve a greater impact on organisational performance.
- It includes some key areas relating to engagement in the workplace and a crucial 3-step guide to assist with the application of engagement analytics.
- Written by Dan Harrison, Ph.D. – Organisational Psychology, developer and CEO of Harrison Assessments, this white paper is a must read for anyone involved in employee engagement. Request your copy here –